What is PRI & How Does It Work?

Summarize this blog with:
Primary Rate Interface (PRI) is a traditional digital telephony service used by businesses to manage multiple simultaneous voice calls over a single physical connection. It is a type of Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) technology that enables reliable, high-quality call handling for organizations with high call volumes, such as call centers and enterprises.
But PRI is more than just a phone line. There are concepts like multiple communication channels, regional trunk types, call signaling, and specific business use cases that determine how PRI actually functions in real-world telecom environments. Understanding these elements is essential to knowing whether PRI is the right solution for your organization.
In this blog, we’ll break down what PRI is, how it works, and the different types of PRI trunk lines. Plus, we’ll explore its advantages and limitations, and how it compares with modern alternatives like Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP), cloud Private Branch Exchange (PBX), and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunking.
Key Highlights:
Primary Rate Interface (PRI) is a digital ISDN-based telecommunication service that enables businesses to handle multiple simultaneous voice calls over a single physical connection with consistent call quality.
PRI works by connecting a company’s PBX system to the PSTN and dividing the connection into B channels for voice/data and a D channel for signaling, ensuring efficient call setup and management.
There are two main types of PRI: T1, commonly used in North America and Japan with up to 23 concurrent calls, and E1, widely used in other regions with support for up to 30 parallel calls.
The key benefits of PRI include secure, high-quality voice communication, compatibility with traditional PBX systems, extended caller ID support, and multiple numbers without extra lines. Likewise, the limitations include higher costs, limited scalability, and reduced flexibility.
Compared to modern alternatives like VoIP, Cloud PBX, and SIP Trunking, PRI offers strong reliability but falls behind in scalability, cost efficiency, advanced features, and support for modern business communication needs.
What is the Meaning of PRI (Primary Rate Interface)?
Primary Rate Interface (PRI) is a digital telecommunication service that allows businesses to make and receive multiple phone calls in parallel over a single physical connection, i.e., copper wire. It is a standardized form of ISDN designed for organizations that require reliable, high-quality voice communication.
In practical terms, PRI acts as the link between a company’s Private Branch Exchange (PBX) system and the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). By dividing a single connection into multiple communication channels, PRI enables efficient call handling for businesses such as offices, call centers, and other large-scale operations, without relying on internet-based calling.
How Does PRI Work?
PRI works by using a single digital connection to manage multiple phone calls, data exchange, or fax signals concurrently. To do this efficiently, the connection is logically divided into different types of channels, each serving a specific purpose. Here are the steps involved: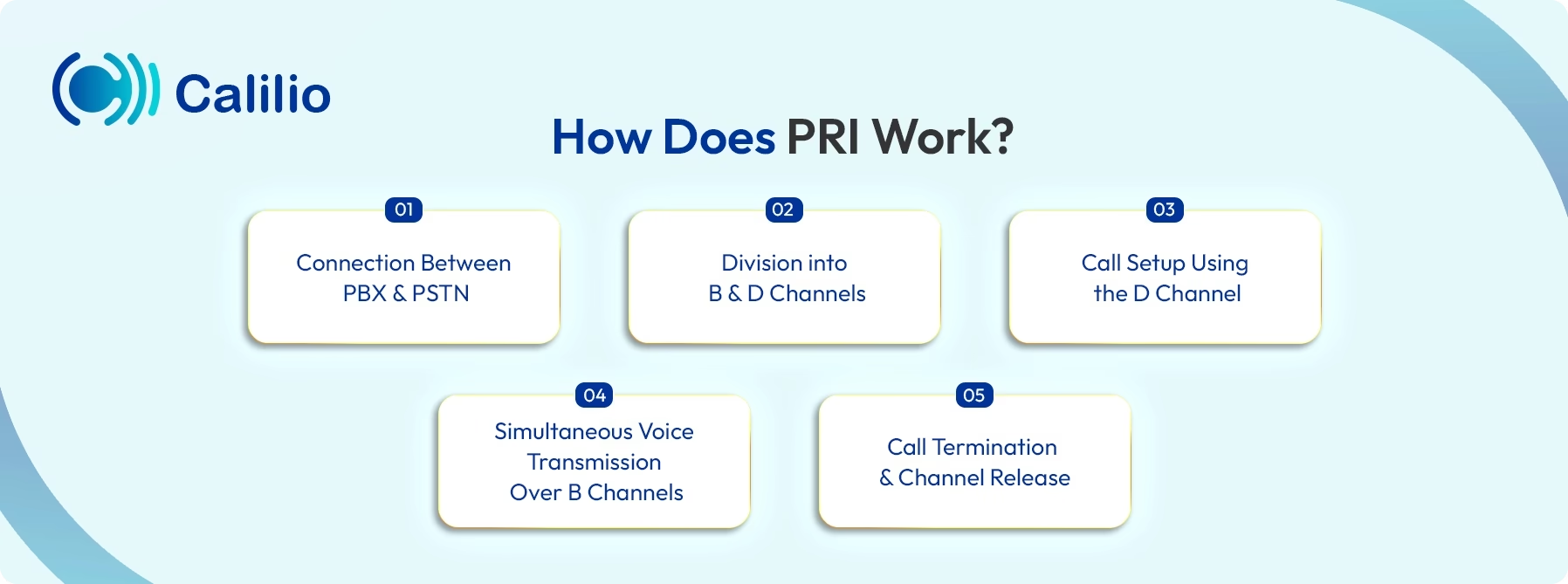
- Connection Between PBX and PSTN
A PRI line creates a dedicated digital link with proper synchronization (clocking) between a business phone system, i.e., PBX, and the public switched telephone network, allowing external voice communication. - Division into B and D Channels
The PRI connection is split into Bearer (B) channels and a Data (D) channel, where:- B channels carry the actual voice or data of a call.
- The D channel handles signaling tasks such as call setup, management, and termination.
- Call Setup Using the D Channel
When a call is initiated, the D channel communicates the necessary signaling information to establish the connection and assign an available B channel. - Simultaneous Voice Transmission Over B Channels
Each active call uses one B channel, allowing multiple calls to occur at the same time without interference. - Call Termination and Channel Release
After the call ends, the D channel signals the system to release the B channel, making it available for new calls.
What are the Types of PRI?
PRI is divided into two types: T1 and E1, based on geographic region and telecom infrastructure. These types determine how many concurrent calls a PRI connection can support as well as where it is commonly deployed.
1. T1
T1-based PRI is primarily used in North America and Japan. It operates at a total bandwidth of 1.544 Mbps, providing 23 B channels for voice or data transmission and 1 D channel for signaling. This configuration supports up to 23 parallel calls, making T1 PRI suitable for medium to large businesses that require stable and predictable call capacity.
2. E1
E1-based PRI is widely used in Europe and most other parts of the world. It offers a higher total bandwidth of 2.048 Mbps, with 30 B channels carrying voice traffic and 1 D channel handling signaling. One additional time slot is reserved for framing and synchronization, ensuring reliable communication. Due to its greater bandwidth and call capacity, E1 PRI is often preferred by enterprises and call centers with high communication demands.
here is the brief comparison between T1 and E1:
Feature | T1 PRI | E1 PRI |
| Primary Regions | North America, Japan | Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia |
| Total Bandwidth | 1.544 Mbps | 2.048 Mbps |
| Total Time Slots | 24 | 32 |
| B Channels (Voice/Data) | 23 | 30 |
| D Channel (Signaling) | 1 | 1 |
| Framing/Sync Slot | Included within the structure | Included within the structure |
| Maximum Simultaneous Calls | 30 calls | 30 calls |
| Typical Use Cases | Medium–large businesses | Enterprises, call centers |
| Call Capacity | Moderate | High |
What are the Advantages of Primary Rate Interface (PRI)?
The benefits of PRI include reliable and secure call handling, high voice quality through dedicated lines, and compatibility with traditional PBX systems. It also supports enhanced caller identification and allows multiple phone numbers without requiring separate physical lines.
- Supports extended caller ID: PRI supports enhanced caller ID functionality for both incoming and outgoing calls, making it easier to identify callers and manage call routing.
- Compatible with traditional PBX systems: PRI works seamlessly with legacy PBX infrastructure, making it a practical option for businesses that rely on on-premise phone systems.
- Secure and reliable communication: Since PRI operates on a circuit-switched network, it bypasses the open internet. Therefore, it offers a dependable and secure option for organizations handling sensitive information like legal and financial firms.
- High-quality voice service: Dedicated physical lines help deliver consistent call quality by minimizing issues such as jitter, latency, and packet loss.
- Multiple numbers without extra lines: With multiple B channels available, businesses can assign individual phone numbers to employees without needing separate physical lines for each number.
What are the Disadvantages of PRI?
The main cons of PRI include high installation and maintenance costs, limited scalability when expanding capacity, and reduced flexibility for remote work compared to modern communication systems.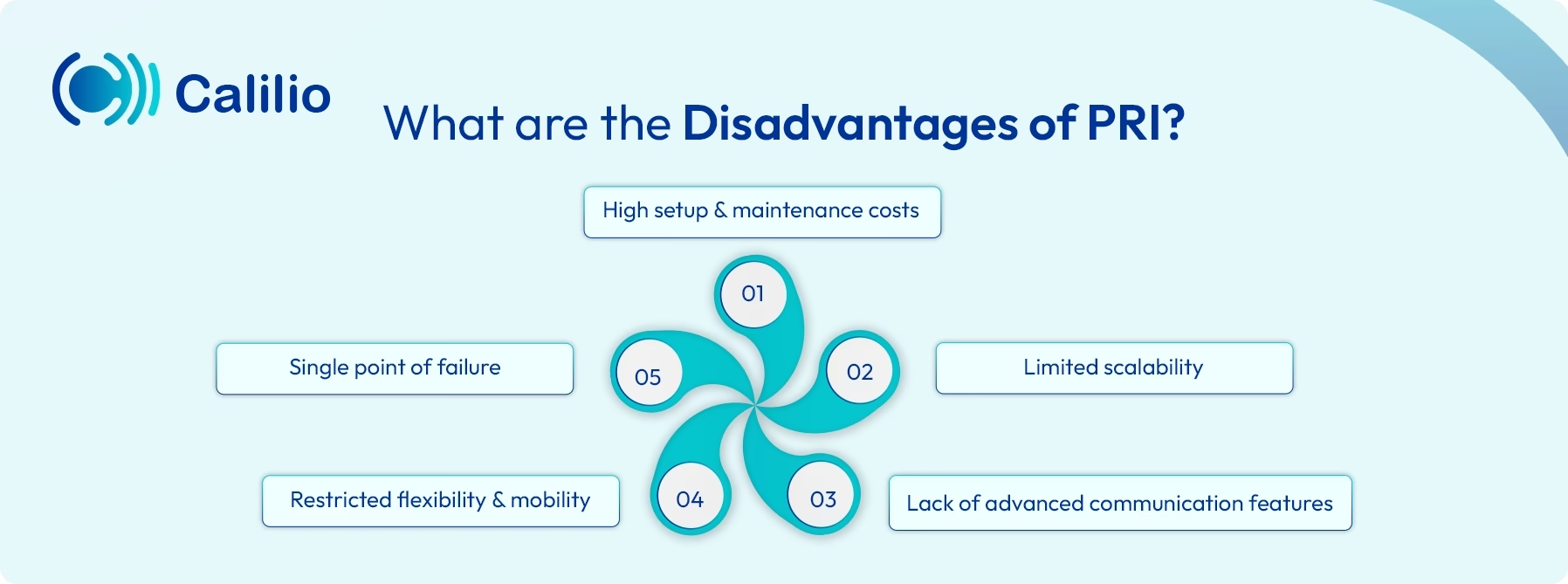
- High setup and maintenance costs: PRI requires physical lines and on-premise equipment, making installation and ongoing maintenance expensive, especially for small businesses.
- Limited scalability: Expanding call capacity often means adding an entire new PRI line, even if only a few additional channels are needed.
- Lack of advanced communication features: PRI does not natively support modern features such as multi-party video conferencing or Unified Communication (UC) that combine calls, messages, and voicemail in one platform.
- Restricted flexibility and mobility: Because PRI is tied to a fixed physical location, supporting remote work or accessing services from different locations can be challenging.
- Single point of failure: Since PRI relies on a physical line into the building, any disruption, such as construction damage, natural disasters, or line faults, can take the entire phone system offline.
PRI vs. Modern Alternatives (VoIP, Cloud PBX, & SIP Trunking)
The key differences between PRI and its modern alternatives, like VoIP, cloud PBX, and SIP trunking, lie in technology, cost, scalability, and flexibility for business use. The table below highlights how these solutions compare across essential factors.
Feature | PRI | VoIP | Cloud PBX | SIP Trunking |
| Technology | Circuit-switched | Internet-based | Cloud-based (VoIP) | IP-based (SIP) |
| Infrastructure Required | Physical lines + PBX | Internet connection | Internet, no on-premise PBX | Internet + IP-PBX |
| Call Quality | Very stable and predictable | Depends on the internet quality | Depends on the internet quality | High call quality with good bandwidth |
| Scalability | Limited | Easy and flexible | Highly scalable | Scales incrementally |
| Installation Cost | High | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Maintenance | Hardware-heavy | Minimal | Minimal | Moderate |
| Advanced Features | Limited | Moderate | Extensive (UC, analytics) | Moderate |
| Remote Work Support | Poor | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
| Best For | Legacy systems, high call stability | Cost-conscious businesses | Modern, distributed teams | Businesses replacing PRI |
Conclusion
Primary Rate Interface (PRI) remains a reliable communication solution for businesses that require stable call quality, secure connections, and compatibility with traditional PBX systems. Its structured, channel-based design makes it especially suitable for organizations handling high call volumes from fixed locations.
However, as business communication needs continue to evolve, modern alternatives such as VoIP, Cloud PBX, and SIP trunking offer far greater flexibility, scalability, and access to advanced features. Among these options, VoIP-based phone systems stand out as the most practical replacement for PRI, as they remove the dependency on physical lines while supporting remote work, unified communications, and cost-efficient growth.
Calilio Introduces Affiliate Program
Earn 30% lifetime commission on every paid referral.
Turn your audience, network, or customers into a recurring revenue stream.

30% recurring commission on every paid referral

Lifetime earnings for as long as the customer stays subscribed

Unique referral link with real-time tracking

Perfect for agencies, consultants, creators, and SaaS partners

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between SIP and PRI?
The main difference between SIP and PRI is that SIP uses a Session Initiation Protocol for transmitting data and can have unlimited voice/data channels. In contrast, PRI uses circuit-switched connections and supports only a limited (24 for T1 and 32 for E1) number of channels in one line.
How many lines are in a PRI?
What is PRI and how does it work?
What are PRI and BRI?
What are the different types of PRI?

Still have questions?
Can’t find the answer you’re looking for? Please chat with our friendly team.
Stay in the loop
Get the latest call insights, trends, and updates delivered straight to your inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive updates from Calilio.
You can unsubscribe anytime.