TCPA Auto Dialer Rules: Everything You Need to Know

Summarize this blog with:
Automated dialing allows businesses to make calls automatically using software or specialized devices, eliminating the need for manual dialing. It’s widely used across sales, marketing, and customer service operations.
However, using auto dialers comes with legal responsibilities. In the US, the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA) enforces strict rules to protect consumers from unsolicited calls. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, lawsuits, and other legal consequences.
To avoid these risks, businesses must clearly understand TCPA auto dialer rules to ensure they operate within the law. This article will cover everything you need to know about TCPA automated dialing laws, including state-specific regulations to help you use auto-dialers responsibly and lawfully.
Key Highlights:
As per TCPA, an auto dialer is a system that stores, generates, and dials phone numbers randomly from the available list.
Under the TCPA rules, businesses must obtain prior written consent before making marketing calls or promotional calls using an auto dialer. They’re also required to follow specific time restrictions and ensure each call includes clear identification of the caller.
Auto dialer regulations may differ from state to state. Different states impose their own requirements and penalties.
Violating TCPA auto dialer rules can lead to fines, lawsuits, reputational damage, and increased scrutiny from regulators like the FCC.
What is an Auto Dialer Under the TCPA?
The TCPA defines an auto dialer as an automatic telephone dialing system (ATDS) that has the capacity to both store or produce telephone numbers using a random or sequential number generator and dial those numbers automatically.
The US Supreme Court states that an auto dialer must have a “random or sequential number generator,” alongside the auto dialing feature, to be considered as an auto dialer under the TCPA.
Furthermore, TCPA imposes strict rules on the use of auto dialers, particularly when it comes to making unsolicited calls to consumers. The law aims to prevent harassment, protect consumer privacy, and ensure that businesses use these systems responsibly.
What are the Key TCPA Auto Dialer Rules Businesses Must Follow?
Businesses must follow TCPA auto dialer rules, such as obtaining written consent before making marketing calls, providing caller identification during each call, and respecting time restrictions. They must also provide an opt-out option, respect Do Not Call lists, and keep accurate records of the calls.
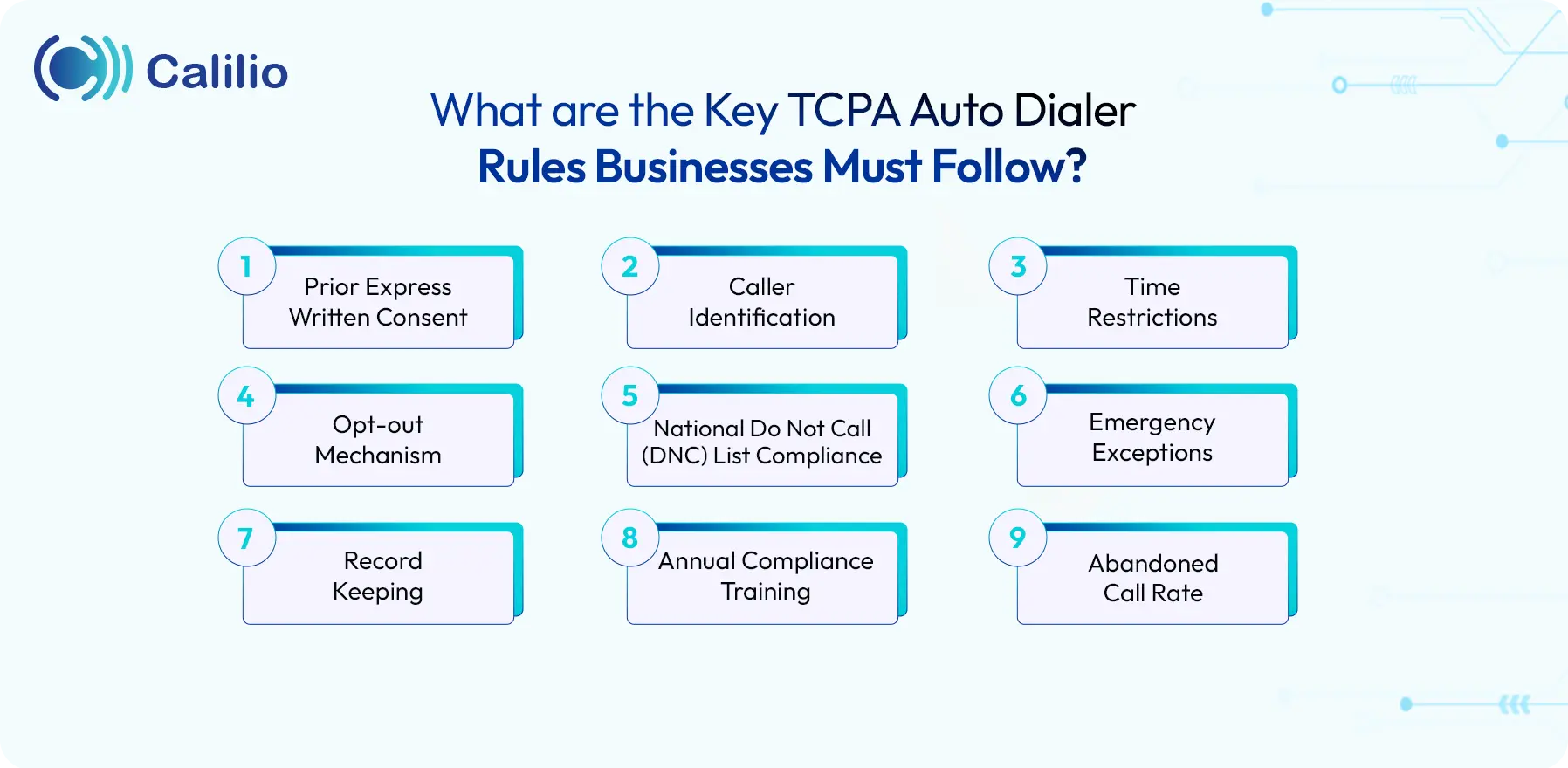
1. Prior Express Written Consent
Businesses must obtain prior express written consent before using an auto dialer to make marketing calls or send text messages to consumers. Businesses can send opt-in messages, clarifying the purpose of calls. Consent must be explicit and should include the type of communication, for example, marketing calls, text messages, etc.
2. Caller Identification
Every call made using an auto dialer or pre-recorded message must provide sufficient information that identifies the business or individual making the call. This typically includes the caller’s name and a contact number or physical address. The purpose is to ensure that recipients can easily identify the source of the call.
3. Time Restrictions
The TCPA restricts the hours during which businesses can make calls using auto dialers or send pre-recorded messages. It requires businesses to make calls only between 8 a.m. and 9 p.m. local time of the recipient. They must avoid calling consumers outside these hours unless the recipient has agreed to receive calls at different times.
4. Opt-out Mechanism
Businesses must include a straightforward opt-out mechanism in every auto-dialed or pre-recorded call. This allows recipients to easily and immediately refuse further communications.
5. National Do Not Call (DNC) List Compliance
If a consumer’s number appears on the National Do Not Call Registry and any state-level DNC lists, businesses must refrain from contacting them unless an existing business relationship exists.
To ensure compliance, businesses must regularly perform DNC scrubbing—the process of removing registered numbers from their call lists. Additionally, businesses must maintain their own internal Do Not Call list to promptly honor any consumer’s requests not to get any calls in the future.
6. Emergency Exceptions
There are some exceptions under the TCPA for calls made in emergency situations. In genuine emergencies, businesses can bypass certain TCPA requirements, such as consent, to deliver urgent messages.
7. Record Keeping
Businesses are required to keep accurate records of their compliance efforts, especially those operating outbound call centers. This includes maintaining documentation of consumer consent, call records, and opt-out requests. Proper record-keeping helps businesses defend against potential legal challenges.
8. Annual Compliance Training
To maintain compliance, businesses can conduct annual training for staff. This training covers TCPA regulations, updates on the law, and best practices for using auto dialers in a compliant manner. Keeping employees informed ensures ongoing adherence to the law.
9. Abandoned Call Rate
The TCPA also sets limits on the call abandonment rate for auto dialers. Abandoned calls are those that are not connected to a live agent. Businesses must ensure that no more than 3% of their calls result in abandonment over a 30-day period. Staying below this threshold is essential for compliance and to avoid penalties.
Auto Dialer Laws by States
While the TCPA sets national guidelines for the use of auto dialers, many states have their own laws that further regulate the use of automated calling systems. These state-specific laws can sometimes be stricter than the federal rules, and businesses need to stay informed to ensure compliance.
Below is a summary of major auto dialer laws in several states, including the key regulations, penalties, and exceptions that apply:
Florida
- Key Regulations: Florida broadly defines auto dialers to include any system that can automatically select or dial numbers and play recorded messages. The state limits auto-dialed calls to 3 attempts per 24 hours per recipient.
- Penalties: $500 per violation; $1,500 per willful violation.
- Exceptions: B2B calls, non-telemarketing calls.
Oklahoma
- Key Regulations: Oklahoma requires prior express written consent for all marketing calls made with auto dialers. Further, calls cannot be made before 8 AM or after 8 PM local time.
- Penalties: $500 per violation; $1,500 per willful violation.
- Exceptions: Calls responding to customer inquiries, political calls, and survey calls.
Washington
- Key Regulations: Callers must identify themselves within the first 30 seconds of the call. If requested, the call must end within 10 seconds.
- Penalties: $100 per violation.
- Exceptions: Calls responding to a request, non-profit calls to active members, polling or opinion calls, and B2B calls.
Indiana
- Key Regulations: Indiana generally prohibits auto-dialed calls without prior consent. Even for playing a recorded message, consent is a must.
- Penalties: $10,000 for the first violation and $25,000 for each subsequent violation.
- Exceptions: Calls from school districts to students, parents, or employees.
California
- Key Regulations: California requires a live person to obtain consent before making automated calls or delivering a prerecorded message. It also prohibits auto-dialed calls to emergency lines, hospitals, and paging services.
- Penalties: $500 per violation; $1,500 per willful violation.
- Exceptions: Some emergency services may be exempt.
Texas
- Key Regulations: Texas mandates express consent for automated calls or texts, especially for marketing or advertising purposes. The Texas Business and Commerce Code also requires consent for call recordings from at least one party involved.
- Penalties: Fines of up to $5,000 per violation.
- Exceptions: Exemptions for business-to-business calls.
New York
- Key Regulations: New York enforces stricter telemarketing rules, including the requirement for a clear and easy opt-out process for future calls.
- Penalties: Up to $20K for violations of telemarketing rules and use of prerecorded messages without written consent.
- Exceptions: Exemptions for certain political and charitable calls.
Illinois
- Key Regulations: The Illinois Automatic Telephone Dialers Act restricts auto dialer use to specific hours (8 am to 9 pm). Callers must clearly disclose the nature of the call and the identity of the organization at the beginning.
- Penalties: $500 statutory damages per violation.
- Exceptions: B2B calls, charitable organizations may have exceptions.
Pennsylvania
- Key Regulations: Pennsylvania requires express written consent for robocalls and automated text messages. It also has protections under the Telemarketer Registration Act, including specific disclosure requirements and restrictions on calling times.
- Penalties: Up to $1000 civil penalty per violation and up to $3K per violation if the recipient is 60 or older.
- Exceptions: Calls made for emergency purposes or to existing customers may have exceptions.
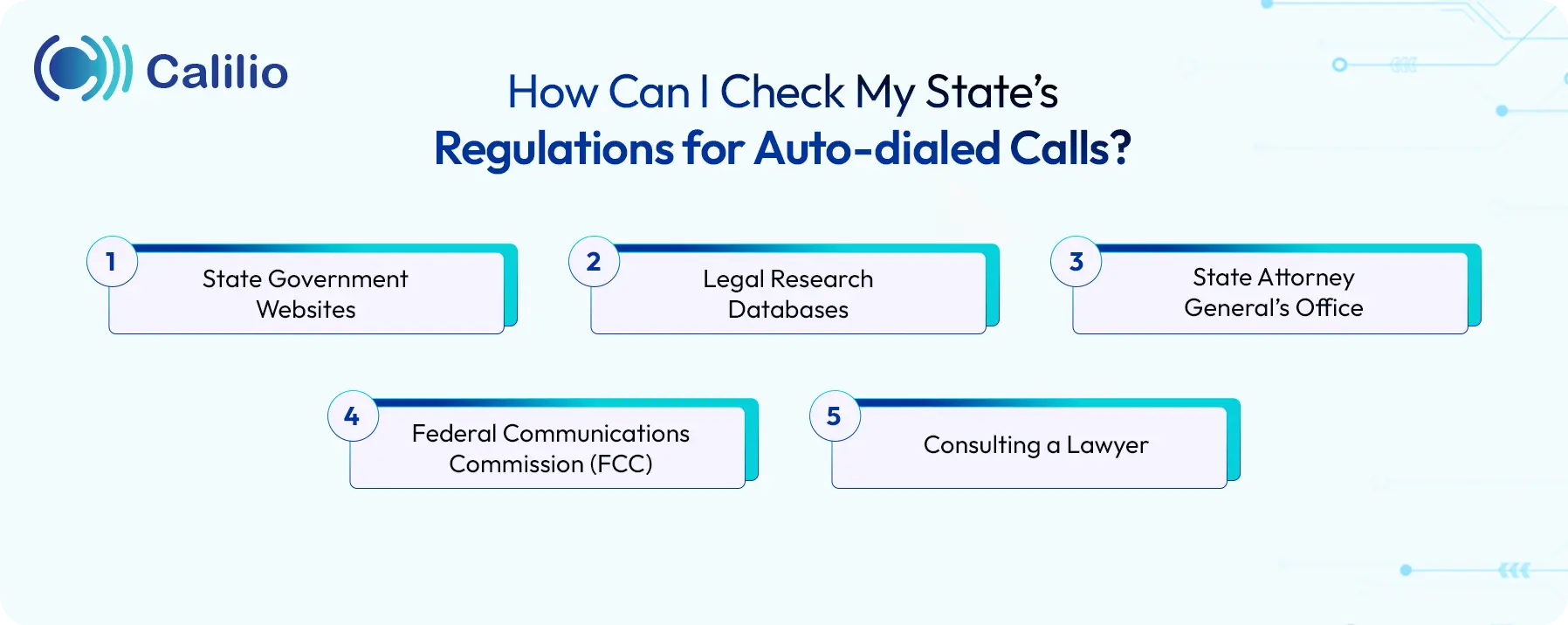
How Can I Check My State’s Regulations for Auto-dialed Calls?
You can check your state’s regulations for auto-dialed calls from your state’s official government website, legal research databases like Westlaw and LexisNexis, and the FCC’s Consumer Protection official site. You can also consult with your State Attorney General or a telecommunications lawyer.
What are the Consequences of Violating TCPA Auto Dialer Rules?
Violating TCPA auto dialer rules can lead to fines, potential lawsuits, and court-imposed restrictions. It can also damage your business reputation and invite further scrutiny from regulators like the FCC.
- Fines and Penalties: Businesses can face fines ranging from $500 to $1,500 per violation. Willful violations can lead to even higher fines.
- Lawsuits and Class Actions: Consumers can file lawsuits for unauthorized auto-dialed calls. And, if many people sue in a class action lawsuit, it can result in very large fines and payments for businesses.
- Reputational Damage: Non-compliance can also harm your company’s reputation, leading to lost trust, negative reviews, and damage to customer relationships.
- Injunctions and Restrictions: If a business violates TCPA rules, courts may order to stop using auto dialers or require the company to follow strict compliance steps, which can disrupt business operations and limit outreach activities.
- Increased Scrutiny from Regulators: Violations can result in heightened scrutiny from agencies like the FCC, leading to investigations and further penalties.
Conclusion
Understanding and adhering to TCPA auto dialer rules is crucial for businesses that use auto dialers for marketing or customer communication. Failing to comply with these rules can lead to significant financial penalties, lawsuits, and reputational damage.
By obtaining proper consent, maintaining updated lists, providing opt-out options, and staying informed about state-specific laws, businesses can ensure they stay compliant and avoid costly penalties.
Calilio Introduces Affiliate Program
Earn 30% lifetime commission on every paid referral.
Turn your audience, network, or customers into a recurring revenue stream.

30% recurring commission on every paid referral

Lifetime earnings for as long as the customer stays subscribed

Unique referral link with real-time tracking

Perfect for agencies, consultants, creators, and SaaS partners

Frequently Asked Questions
What types of calls fall under TCPA auto dialer rules?
Calls made using an auto dialer for marketing, promotions, advertisements, or surveys fall under TCPA rules. This includes both robocalls and voice calls.
Do international calls need to follow TCPA rules?
What tools can help with auto dialer compliance?
Is it legal to use an auto dialer for business calls?
What if my auto dialer only calls numbers from a contact list?

Still have questions?
Can’t find the answer you’re looking for? Please chat with our friendly team.
Stay in the loop
Get the latest call insights, trends, and updates delivered straight to your inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive updates from Calilio.
You can unsubscribe anytime.