What is DSL? A Comprehensive Guide 2026

Slow loading pages, dropped connections, and inconsistent speeds can turn simple online tasks like video calls, streaming, or remote work into daily frustrations. These issues often occur when multiple users share the same network line or when the connection isn’t built to handle peak-hour traffic.
This is where DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) stands out. It delivers internet through existing telephone lines but uses a dedicated point-to-point channel, ensuring stable speeds, minimal congestion, and reliable performance even when the network is busy.
In this guide, we’ll break down what DSL internet is, how it works, the different types, and the key benefits it offers for both homes and businesses. You’ll also learn how to set it up and how it compares with other internet technologies.
Key Highlight
DSL acts as a dedicated point-to-point channel, minimizing congestion and maintaining stable internet speeds.
DSL works by dividing frequency bands, modulating data through a DSL modem, and transmitting it via copper lines to the service provider.
There are six main DSL types: HDSL, SDSL, ADSL, SHDSL, VDSL, and VDSL2, each optimized for different speed, distance, and usage requirements.
DSL’s benefits include always-on connectivity, affordability, reliability, and easy setup without new cabling.
DSL stands out for its reliable performance and broad accessibility, unlike cable or wireless networks affected by shared bandwidth or weather conditions.
Setting up a DSL connection involves installing a splitter, connecting a DSL modem, configuring ISP settings, and securing your network for reliable access.
What is DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) Internet?
DSL internet is a broadband internet technology that delivers high-speed internet access through existing telephone lines. It enables simultaneous internet and voice calls over a single line by transmitting digital signals, ranging between 0–4 kHz and above 25 kHz for voice & data, respectively.
Beyond being a simple connection method, DSL technology acts as a dedicated point-to-point channel managed by a network service provider. It minimizes network congestion, maintains stable connection speeds, and supports continuous high-speed internet access even during peak usage hours.
How Does DSL Work?
DSL splits voice and data into separate frequency bands, converts your digital signals, sends them through the local loop, processes them at the provider’s DSLAM, and returns decoded data to your modem, creating a continuous, stable internet connection.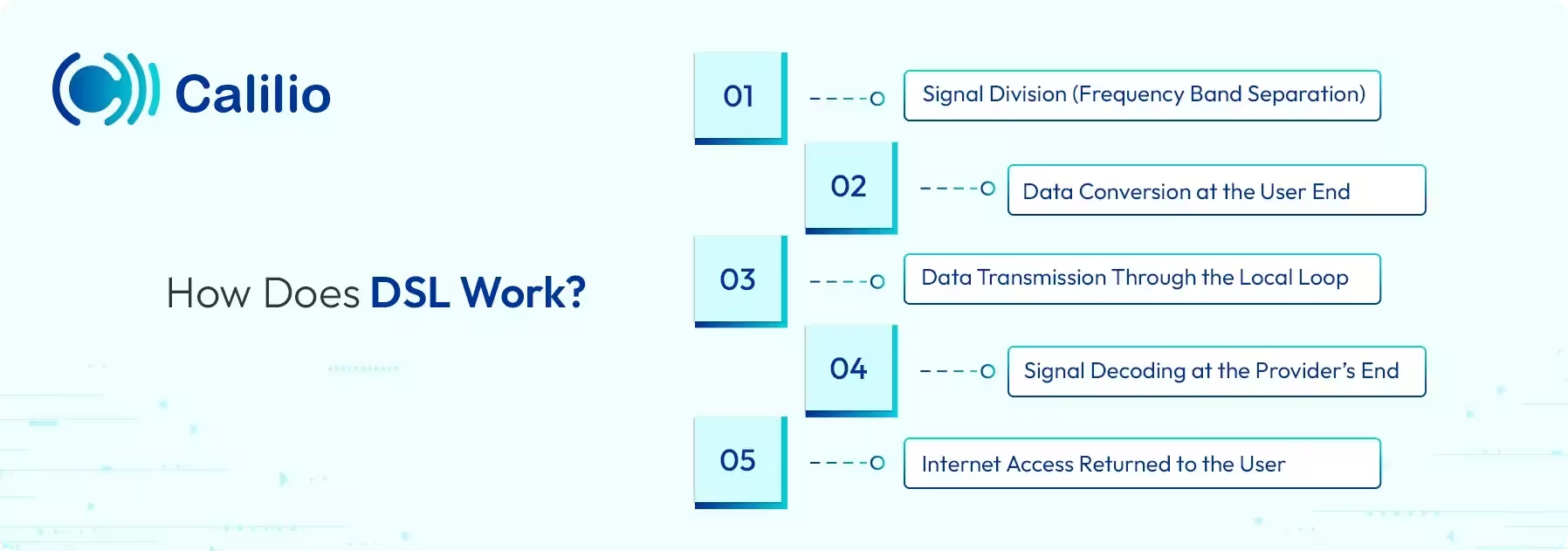
1. Signal Division (Frequency Band Separation)
The DSL line splitter divides the telephone line into two frequency channels, such as low frequencies (0–4 kHz) for voice and higher frequencies (25 kHz and above) for internet data transmission.
2. Data Conversion at the User End
Next, the DSL modem converts digital data from connected devices into electrical signals that travel through copper telephone wires. This process enables seamless data transmission to your internet service provider.
3. Data Transmission Through the Local Loop
Once modified, the electrical signals travel through the local loop network, a copper wiring that connects to the network service provider’s central office. This dedicated link between the user and provider helps maintain a consistent and secure point-to-point DSL connection.
4. Signal Decoding at the Provider’s End
At the network service provider’s central office, the DSL Access Multiplexer (DSLAM) receives and demodulates signals, separating voice and internet data. It then routes processed information through the DSL network backbone for delivery.
5. Internet Access Returned to the User
Finally, the processed data travels back through the same DSL connection to your DSL modem. The modem then demodulates the signals, converting them into digital data for your devices, delivering a high-speed internet experience through a single telephone line.
What are the Types of DSL?
There are 6 types of DSL: HDSL, SDSL, ADSL, SHDSL, VDSL, & VDSL2. They are categorized based on their speed, usage (for homes or businesses), and the balance between upload and download speeds.
1. HDSL (High-Bit-Rate Digital Subscriber Line)
HDSL provides symmetrical high-speed data transmission using two pairs of copper wires, maintaining equal upload and download rates over medium distances. It is ideal for business networks requiring stable and consistent high-capacity telephone connectivity.
2. SDSL (Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line)
SDSL delivers equal upstream and downstream speeds through a single pair of copper wires for reliable point-to-point communication. It’s widely used in business environments where consistent data transfer and secure network performance are essential.
3. ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line)
ADSL enables faster download speeds than upload speeds, making it suitable for home users and small offices focused on browsing, streaming, and downloading. Its wide bandwidth allocation supports smooth multimedia and data-intensive online activities.
4. SHDSL (Single-Pair High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line/G.SHDSL)
SHDSL offers symmetrical data rates across one or more copper pairs, supporting speeds up to 5.7 Mbps per pair. It’s optimized for enterprise Local Area Network (LAN) extensions, Private Branch Exchange (PBX) systems, and private networks that require high-quality, long-distance connectivity.
5. VDSL (Very-High-Bit-Rate Digital Subscriber Line)
VDSL delivers ultra-fast internet speeds up to 52 Mbps downstream and 16 Mbps upstream over short distances. It supports voice, data, and video transmission simultaneously, making it ideal for high-definition TV, video conferencing, and multimedia streaming.
6. VDSL2 (Very-High-Bit-Rate Digital Subscriber Line 2)
VDSL2 provides symmetrical speeds up to 100 Mbps and maintains strong performance over longer copper loops. It powers triple-play services, such as data, voice, and video, offering fiber-like speed through existing copper infrastructure.
What are the Benefits of DSL?
DSL delivers a reliable and always-on internet connection with stable speed for uninterrupted browsing and communication simultaneously. It remains an affordable, widely available, and easy-to-install broadband option, offering dependable performance for both home users and businesses.
- Always-On Internet Connection: A DSL connection keeps your devices connected to the internet at all times. This ensures instant and uninterrupted internet availability for daily use.
- Simultaneous Voice and Data Transmission: DSL technology separates the frequency of voice and data signals, allowing you to browse the internet and make calls simultaneously.
- Cost-effective Internet Solution: DSL internet uses existing copper telephone lines, eliminating the need for expensive new wiring. It offers affordable broadband access compared to fiber or satellite services.
- Stable Internet Speed: As DSL is a dedicated point-to-point connection, it provides consistent internet speeds, unaffected by nearby users’ traffic.
- Wide Availability: DSL services are available in most areas where telephone lines exist, making it accessible to both urban and rural users without major infrastructure upgrades.
- Easy Installation and Setup: You can quickly connect to DSL using standard phone jacks without requiring specialized equipment or complex configurations.
- Suitable for Home and Business Use: With different DSL types like ADSL and VDSL, you can choose the option that best fits your speed, distance, and usage requirements. ensuring optimal performance for your internet needs.
What Sets DSL Apart from Other Internet Connections?
Here’s a detailed insight into how DSL compares with cable, fiber, fixed wireless, and dial-up internet:
DSL Vs. Cable
Cable internet speeds can fluctuate depending on how many people share the network. On the other hand, DSL provides a dedicated connection for each user, ensuring more consistent performance and stable speeds, even in peak hours.
ASPECTS | DSL | Cable |
| Data Delivery | Uses telephone lines for data transmission | Uses coaxial cable lines for data transmission |
| Speed | Generally offers up to 100 Mbps | Can offer speeds up to 1 Gbps |
| Bandwidth Sharing | No, offers dedicated bandwidth | Yes, bandwidth is shared among neighborhood users |
| Availability | Widely available | Limited availability, especially in rural areas |
| Consistency | Speeds are consistent and not affected by peak times | Speeds can fluctuate during peak usage times |
| Installation | Can use existing phone lines, simpler setup | May require professional installation |
| Cost | Often more affordable, especially for moderate-speed plans | Can be higher, especially for high-speed plans |
DSL Vs. Fiber Optic
Fiber optic internet offers higher speeds and requires limited infrastructure, but it often requires costly installation. In contrast, DSL internet uses existing telephone lines, making it more accessible and affordable for most homes and small businesses.
ASPECTS | DSL | Fiber Optic |
| Technology | Uses copper telephone lines | Uses fiber optic cables for data transmission |
| Speed | Up to 100 Mbps | Up to 1 Gbps or higher |
| Bandwidth | Limited by the quality and length of copper lines | Higher bandwidth, allowing for faster data transmission |
| Reliability | Connectivity quality degrades over long distances from the service provider | Distance doesn’t impact connectivity |
| Availability | Broad availability | Limited to areas with fiber infrastructure in place |
| Latency | Higher latency due to electrical signal interference | Very low latency, ideal for gaming, streaming, and real-time communication |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Can be more expensive due to newer technology and installation costs |
DSL vs. Fixed Wireless Internet
Fixed wireless connections depend on signal strength and weather conditions, which can affect reliability. However, DSL delivers uninterrupted high-speed connectivity through wired copper lines, ensuring steady performance regardless of location or weather.
Aspects | DSL | Fixed Wireless |
| How it works | Uses copper phone lines to deliver the internet | Sends internet from a tower to your home using a wireless signal |
| Speed | Up to 100 Mbps | 5 to 50 Mbps (can vary with weather or signal strength) |
| Where it works | Areas with landline phone service | Rural or remote places without phone or cable lines |
| Reliability | Stable, but the signal weakens the farther you are from the provider | Can be affected by rain, fog, or buildings blocking the signal |
| Cost | Usually cheaper, especially in cities | Often costs more due to setup and limited providers |
| Installation | Needs a DSL modem and phone line filters | Quick setup with a receiver aimed at the tower |
DSL vs. Dial-up
ASPECTS DSL Dial UPConnection Type Digital over telephone lines Analog over telephone lines Speed Up to 100 Mbps Up to 56 Kbps Phone Line Usage Internet and phone services can be used simultaneously Occupies phone line while in use Reliability More reliable, with consistent speeds Less reliable, susceptible to noise and disconnections Cost Higher than dial-up but offers better speed and reliability Lower, but significantly slower and less convenient Set-up Requires a DSL modem to install Requires a dial-up modem to install
How to Set Up a DSL Connection?
To set up a DSL connection, you need to install a DSL splitter on your telephone line, connect the DSL modem and configure it with the internet service provider’s settings. Once set up, secure your network with a strong password for safe and reliable internet access.
Step 1: Contact a DSL Internet Service Provider
Choose a reliable DSL service provider in your area and request activation for your DSL line. The provider will confirm line compatibility and supply any required equipment.
Step 2: Install the DSL Splitter (Filter)
Attach a DSL splitter to your existing telephone line. This separates voice and data signals, allowing you to make calls and use the internet simultaneously without interference.
Step 3: Connect the DSL Modem or Router
Plug your DSL modem or router into the splitter’s data port using the provided cable. This device converts the incoming digital subscriber line signals into internet data for your devices.
Step 4: Power On and Configure the Modem
Turn on the DSL modem, connect it to your computer via Ethernet or Wi-Fi, and open a browser. Enter the login credentials or configuration settings given by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Step 5: Test the DSL Connection
Check the DSL indicator light on your modem. When it’s steady, your line is active. Run a quick speed test to ensure your DSL connection is stable and performing correctly.
Step 6: Secure Your Network
Set a strong Wi-Fi password, enable encryption, and change the default admin login to keep your DSL network safe from unauthorized access.
Conclusion
DSL has remained a reliable broadband option for years, delivering stable internet through existing telephone lines without the need for major infrastructure upgrades. By separating voice and data into different frequency bands, it provides a continuous, congestion-free connection.
And with multiple options, such as ADSL, VDSL, SHDSL, and VDSL2, you can choose the DSL variant that best matches your speed requirements, distance limits, and daily usage.
Summarize this blog with:
Frequently Asked Questions
Is DSL affected by weather conditions?
DSL internet is affected less by weather than wireless or satellite connections since it runs through insulated copper telephone lines. However, extreme weather like heavy storms or flooding can occasionally impact connection quality or line stability.
What is DSL used for?
Can I use DSL if I have multiple devices connected to the internet?
Can I use DSL in conjunction with other internet services?
How is DSL different from WiFi?
Is DSL internet fast enough?
What is the application of DSL?

Still have questions?
Can’t find the answer you’re looking for? Please chat with our friendly team.
Stay in the loop
Get the latest call insights, trends, and updates delivered straight to your inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive updates from Calilio.
You can unsubscribe anytime.
