VoIP Latency: What It Is, Why It Happens, and How to Fix It

You’re on a call with a client, and suddenly your voice starts breaking or there's a delay in response. This delay, known as VoIP latency, can ruin essential conversations. Whether you're running a business or just catching up with someone, such interruptions can create awkward pauses, reduce communication quality, and cause frustration.
To fix the issues, first, you must understand latency in VoIP communication and its root causes. Then, with a few simple fixes, you can transform your laggy calls to clear and natural ones.
In this guide, we will explore what VoIP latency is, how to measure it, its causes, and provide easy solutions, so every call sounds smooth and professional.
Key Highlights:
VoIP latency is the delay between when a voice packet is sent and when it is received during an internet call.
You can measure latency using tools like ping tests, traceroute, and specialized VoIP speed tests.
VoIP latency causes delays in conversations, leading to choppy audio, overlapping speech, echoes, and poor communication flow.
Common causes include crowded networks, weak Wi-Fi, outdated equipment, poor voice encoding, and inefficient routing.
Troubleshooting involves improving internet connections, switching to wired setups, updating devices, and optimizing network paths.
What Is VoIP Latency?
VoIP latency is the delay between when you speak and when the other person hears your voice during an internet call. During the online call, your voice is converted into digital data that travels across multiple network connections before being reassembled and converted back into sound at the other end. The longer this process takes, the more noticeable the delay becomes.
Since VoIP transmits voice data in real-time through continuous packet exchanges, minimal latency is crucial for achieving a clear, uninterrupted call. Even a small delay makes a call feel unnatural or creates noticeable pauses, degrading call quality and communication.
What are the Different Types of VoIP Latency?
The primary types of VoIP latency include one-directional latency and round-trip latency.
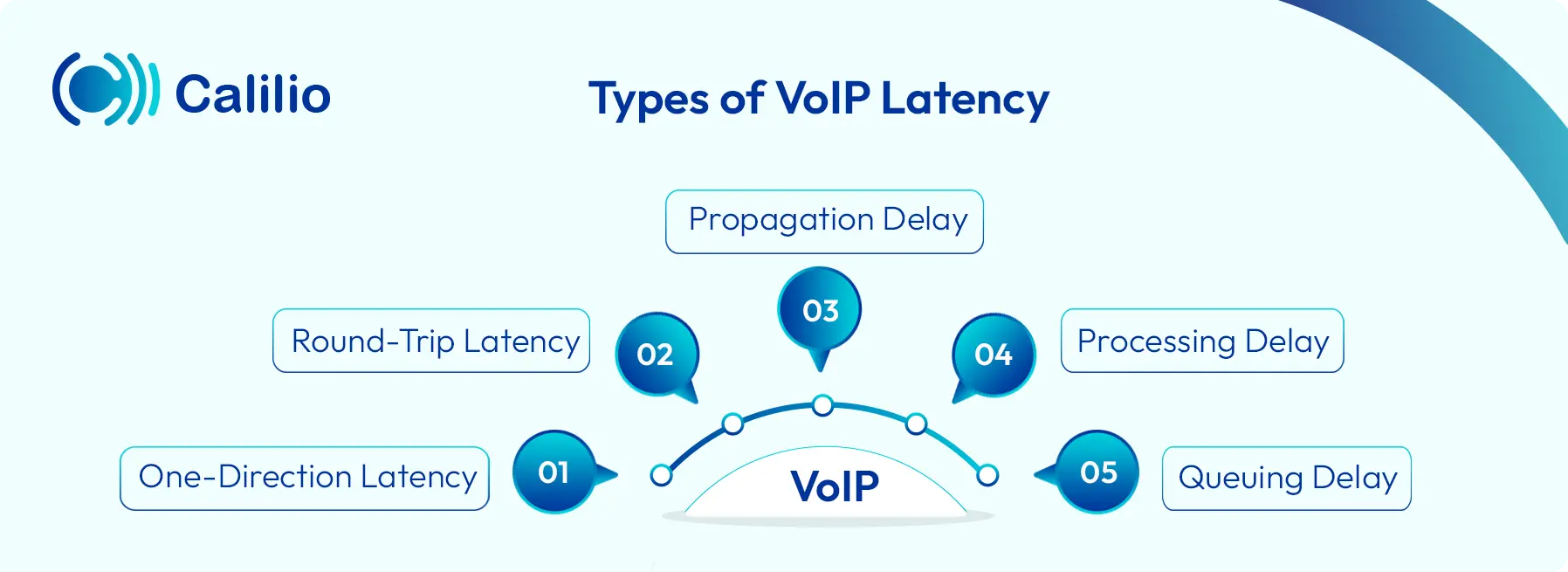
- One-Direction Latency: It’s also known as one-way delay, which represents the time it takes for a data packet to travel from its starting point to its destination.
- Round-Trip Latency: It’s the total time it takes for a data packet to travel from your device to a server and back with a response.
There are a number of reasons for both one-way and round-trip delays in VoIP communication. These include:
- Propagation Delay: It is the time it takes for data to physically travel through cables or signals across the internet. The longer the distance, the higher the delay.
- Processing Delay: It is the time your devices need to convert your voice into digital signals and back again. Slow or overloaded hardware can increase this delay.
- Queuing Delay: It is the wait time for voice packets in a router or switch when the network is busy. This hold-up happens when many users share limited bandwidth.
What Is the Acceptable Latency for VoIP?
The latency threshold for VoIP is typically below 150 milliseconds (ms). Latency below 20 ms is ideal for clear VoIP calls, while anything above 300 ms is unacceptable for VoIP calls and impacts call clarity and responsiveness.
- Under 50 milliseconds (ideal): Callers chat as if they were in the same room, and almost no one feels any delay.
- Under 150 milliseconds: Your calls sound natural with little to no delay.
- 150 to 300 milliseconds: You may notice slight pauses, but conversations stay mostly smooth.
- 300 to 400 milliseconds: Delays become distracting and can interrupt the flow of talk.
- Above 400 milliseconds: Communication feels slow and frustrating, making conversations difficult.
How is VoIP Latency Measured?
You can test VoIP audio delay using tools like ping, traceroute, VoIP test sites, or network monitoring apps. The delay is measured in milliseconds (ms), which represents the time for the data packet to travel from one end to another.

I. Ping Test
The ping command provides latency information for a specific IP address. It sends a small data packet to a remote server and measures how long it takes to return. While it doesn't show full VoIP path latency, it quickly reveals basic network delays. You can run this test using a ping command in the Command Prompt for Windows or the Terminal for Mac and Linux.
II. Traceroute
Traceroute is a network diagnostic tool that maps the full journey of packets from your device to the destination. It shows each step your voice data takes to reach the other end. It helps identify where the latency occurs in the network, whether it’s in your local router, ISP, or internet path.
III. VoIP Speed Test Tools
VoIP testing tools simulate voice calls to measure real-time performance indicators like latency, jitter, and packet loss. They give more accurate results about the call quality of VoIP. PingPlotter and SolarWinds VNQM are popular VoIP speed test tools.
IV. Network Monitoring Software
Some apps, such as PRTG, SolarWinds, and Wireshark, track your network in real time. They capture and analyze individual VoIP packets to measure packet delay, jitter, and loss in detail. This helps you catch spikes in delay and fix them before they ruin your call quality.
Upgrade Your Voip Phone System for Crystal Clear Calls - No More Delays or Interruptions!
How VoIP Latency Disrupts Communication?
VoIP latency can cause voices to overlap, create echo, or miss words. It makes conversation slow and choppy, causing unsynchronized audio.
- Slow and Interrupted Conversations: Latency causes delays in speech delivery, making conversations feel sluggish and fragmented.
- Overlapping Noises: Delayed audio can lead both people to speak at the same time, creating confusion and overlapping voices.
- Echoes: Latency may cause your voice to bounce back into your ear with a delay, which is distracting.
- Synchronization Issues: Latency leads to poor timing between what is said and what is heard. This lack of sync disrupts the flow of conversation.
- Reduced Communication Bandwidth: High latency slows down data flow, causing delays and limiting how much information can be sent smoothly at once.
- Lag in Online Activities: It slows down real-time online actions like screen sharing, video meetings, or file transfers during the call.
What Causes Latency in VoIP and How to Fix It?
Latency in VoIP happens because of network congestion, weak wireless connections, outdated hardware, and slow voice processing. You can fix these VoIP issues by improving your internet speed, using wired connections, upgrading devices, and updating your VoIP software.
1. Overloaded Networks
When too many devices use the same internet connection, the network becomes congested and slows down data transmission. This delays voice packets, causing poor call quality and noticeable audio lag.
Fix:
- Reduce non-essential internet usage during calls.
- Prioritize VoIP traffic using Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router.
- Invest in an SD-WAN or similar network optimization to improve call quality.
2. Wireless Connections
Wi-Fi connections are more vulnerable to interference, signal drops, and packet loss, which can increase latency. Wireless networks also tend to have higher jitter compared to stable wired connections.
Fix:
- Use a wired Ethernet connection for important calls.
- Test your Wi-Fi speed to ensure its signal strength.
- Move closer to the router or reduce interference by switching channels.
3. Outdated or Damaged Hardware
Old routers, switches, or worn-out cables cannot process or transmit data efficiently, leading to delays in VoIP communication. Faulty hardware often drops or misroutes packets, further affecting call clarity.
Fix:
- Regularly inspect and replace faulty cables and devices.
- Update your hardware drivers and firmware.
4. Suboptimal Voice Encoding
VoIP providers use VoIP codecs to compress audio data for efficient and high-quality voice communication over the internet. However, using an inefficient or poor codec increases processing time, causing latency.
Fix:
- Contact your VoIP provider to check if your current codec is optimal.
- Switch to recommended codecs like G.711 or Opus for better quality and speed.
- Test calls after codec changes to confirm improvement.
5. Incorrect Network Setup
Misconfigured firewalls, Network Address Translation (NAT) settings, or missing port forwarding rules can block or delay VoIP traffic. It causes packets to reroute or drop, resulting in echo, lag, or dropped calls.
Fix:
- Use tools like traceroute or network path analysis to identify misconfigured points.
- Restart routers and modems regularly to refresh network paths.
Conclusion
VoIP latency delays data transmissions, which negatively impacts call quality. It often happens due to an unstable internet connection, outdated hardware, or software issues. Using wired connections, updated hardware, and proper network settings helps reduce delays.
Summarize this blog with:
Frequently Asked Questions
How much latency is bad for a voice call?
For voice calls, latency above 150 milliseconds (ms) can start to noticeably affect call quality. Latency over 200–250 ms results in a bad phone call quality, as it can lead to delays, overlapping speech, and difficulty holding a natural conversation.
Can using Wi-Fi increase VoIP latency?
Which is better between jitter and latency?
What is the minimum latency for VoIP?

Still have questions?
Can’t find the answer you’re looking for? Please chat with our friendly team.
Stay in the loop
Get the latest call insights, trends, and updates delivered straight to your inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive updates from Calilio.
You can unsubscribe anytime.
