Trunk Line: Types, Benefits, Implementation & Challenges

Summarize this blog with:
As your business grows, so does the number of incoming and outgoing calls. Relying on separate phone lines for every employee leads to busy signals, dropped calls, rising expenses, and a messy phone setup.
A trunk line offers a smarter alternative. By carrying multiple calls through a single connection, it simplifies communication, reduces hardware needs, and supports fast, seamless scaling.
In this guide, you’ll learn what a trunk line is, how it works, its types and why modern businesses now prefer VoIP trunk lines.
Key Highlights:
A trunk line is a shared communication pathway that carries multiple calls at once, helping businesses replace individual phone lines with a centralized system.
Businesses can choose from analog, digital, and SIP/VoIP trunk lines, each offering different levels of capacity, flexibility, and technology.
Setting up VoIP trunks involves selecting a provider, adding SIP credentials to your PBX, configuring routing rules, and testing call flow.
VoIP-based SIP trunks cut costs, improve call quality, and allow flexible routing and instant scalability without new wiring or hardware.
Traditional trunk line faces issues like physical dependency, limited scalability, and higher upgrade costs, whereas SIP or VoIP trunk lines depend on stable internet and proper security.
What is a Trunk Line?
A trunk line is a communication pathway that carries multiple phone calls at the same time through a single shared connection. Instead of assigning one dedicated line to each user, businesses use trunk lines to bundle several calls together, making their phone system more efficient and cost-effective.
In traditional telephony, trunk lines connected different telephone exchanges, allowing calls to travel between regions and networks efficiently. Modern trunking works the same way but uses digital technologies like SIP and VoIP trunk lines. These versions send calls over the internet instead of copper cables, giving businesses better call quality, faster routing, and the ability to manage calls from multiple locations through one centralized system.
How Does a Trunk Line Work?
A trunk line carries several calls through one shared connection instead of using a separate line for each phone. When you make or receive a call, your PBX system sends the call into the trunk, and the system assigns it to an open channel inside that connection. If channels are available, calls pass through without delay. When all channels are busy, new callers may hear a busy tone.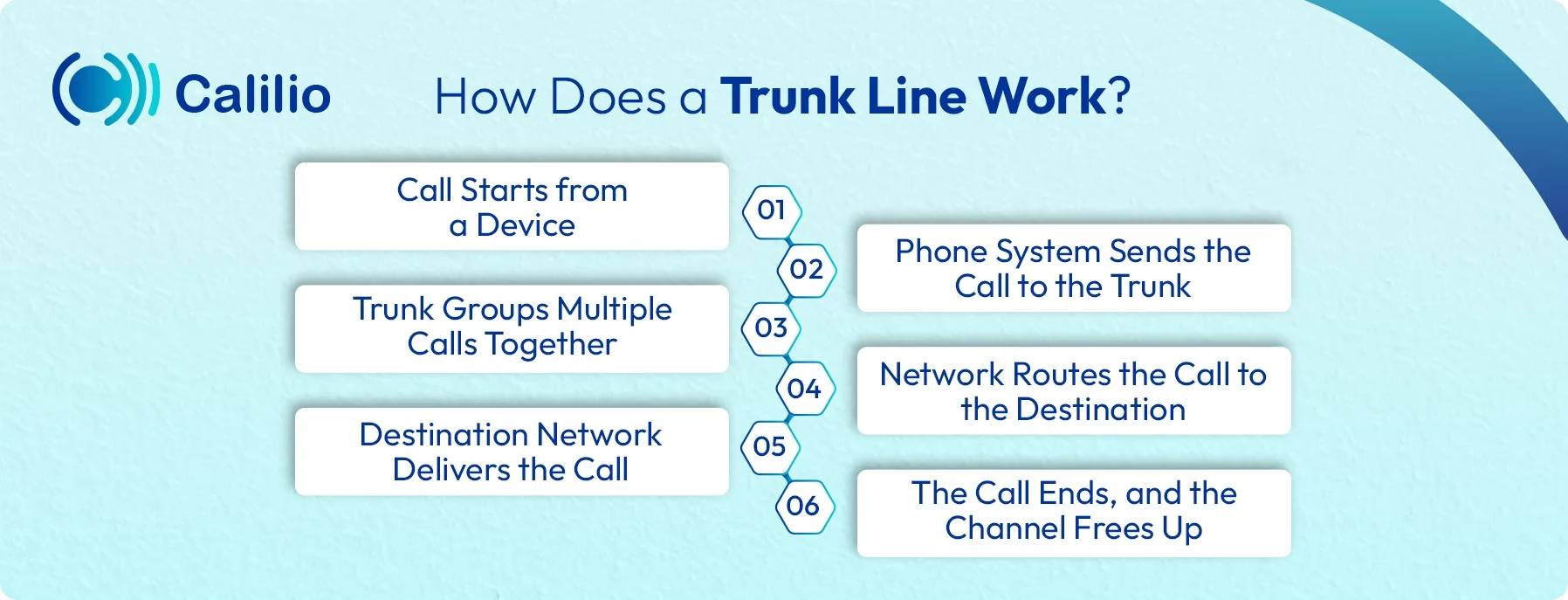 Here is the step-by-step process of how trunk lines work in a modern phone system:
Here is the step-by-step process of how trunk lines work in a modern phone system:
- Call Starts from a Device: A user dials a number from a desk phone, softphone, or mobile app connected to the phone system.
- Phone System Sends the Call to the Trunk: The PBX or cloud phone system receives the call and sends it to the trunk line instead of a direct, single line.
- Trunk Groups Multiple Calls Together: The trunk groups this call with other active calls and sends them over the same shared channel or internet connection.
- Network Routes the Call to the Destination: The trunk connects to the telecom carrier or VoIP provider. The provider then carries the call across its network to the destination number.
- Destination Network Delivers the Call: The call reaches the recipient’s carrier or VoIP provider, which then connects it to the person being called.
- The Call Ends, and the Channel Frees Up: When the call ends, the channel on the trunk becomes free and can be used for the next call.
Types of Trunk Lines
The various types of trunk lines include analog, digital, and SIP trunk lines. Analog and digital trunks are the traditional options, while SIP trunking is VoIP-based trunking that works through the internet.
Analog Trunk Lines
An analog trunk uses copper wires to carry voice signals and connects directly to a business PBX. They support only one call per line, so companies need multiple lines if they want to handle several simultaneous calls.
These lines are common in older PBX systems and provide basic calling features and stable voice quality, but they lack the scalability and flexibility offered by modern options.
Digital Trunk Lines
A digital trunk line is the upgraded version of older analog lines. It uses digital signaling instead of raw analog voice, which allows one physical connection to carry many calls at the same time.
The most common digital trunks are T1 and E1 lines, where a T1 supports 24 channels and an E1 supports 30 channels.
Each channel represents one call, which means a single digital trunk line can replace dozens of individual analog lines. This gives a business more call capacity through one connection while reducing the need for multiple cables running into the PBX.
SIP Trunks (VoIP-based Trunks)
A SIP trunk is the modern version of a trunk line that runs over the Internet instead of copper or digital circuits. It sends voice as data through a stable internet connection, so there’s no need for separate physical lines for each call. When a provider delivers and manages these connections, that service is called SIP trunking.
A SIP trunk can support as many channels as your provider and bandwidth allows, and each channel works as a single call path. You can add or remove channels within minutes, which makes it easy to handle changes in call volume. Since it works with IP-PBX systems and eliminates the need for on-site lines, a SIP trunk offers clearer audio, easier scaling, and lower costs compared to older trunk line setups.
How to Set Up SIP/VoIP Trunk Lines?
To set up VoIP trunk lines, choose a provider that supports SIP trunking, create an account, and get your trunk credentials. Add these SIP details to your PBX or cloud phone system, set your routing rules, and test calls to confirm everything works. After that, your VoIP trunk is ready for daily call traffic.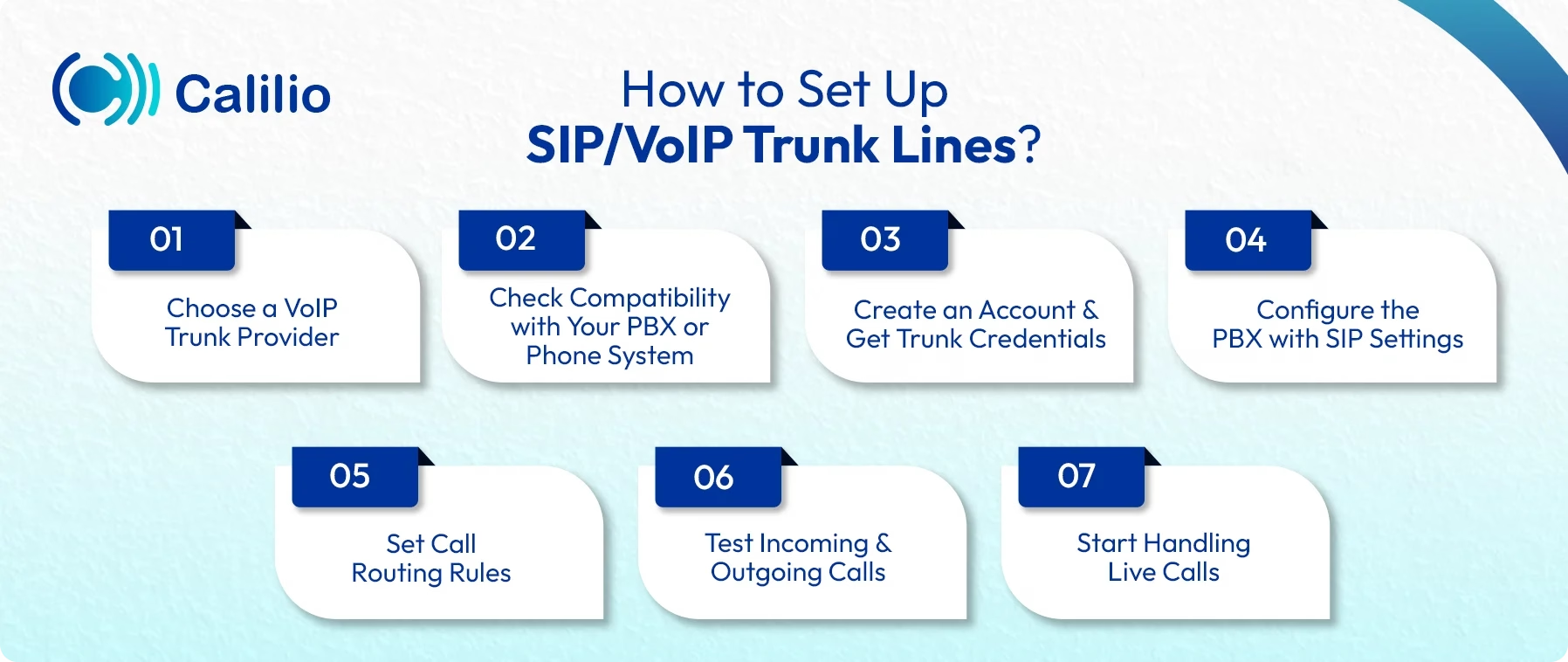
1. Choose a VoIP Trunk Provider
Select a provider that supports SIP or VoIP trunking, offers reliable uptime, and fits your call volume needs. Also, decide how many SIP trunk lines you need based on your call volume.
2. Check Compatibility with Your PBX or Phone System
Make sure your current PBX, whether it’s on-premise or cloud-based, can connect to SIP or VoIP trunk lines. Most modern systems support this integration easily.
3. Create an Account and Get Trunk Credentials
Sign up on the provider’s platform and get SIP credentials. These include the server address, username, password, and port details needed to connect your PBX to the trunk.
4. Configure the PBX with SIP Settings
Enter the trunk credentials into your PBX or cloud phone system. This connects your internal call setup to the provider’s network so external calls can pass through the trunk.
5. Set Call Routing Rules
Define how outbound calls should use the trunk and how inbound calls should reach your extensions. This includes failover routing, forwarding rules, and caller ID settings.
6. Test Incoming and Outgoing Calls
Make a few calls to confirm audio quality, routing accuracy, and stability. Adjust settings if needed to ensure a smooth call flow.
7. Start Handling Live Calls
Once everything works smoothly, your VoIP trunk lines are ready for daily use. Your team can now handle multiple calls without relying on physical phone lines.
Benefits of Using VoIP-based SIP Trunk Lines
VoIP-based SIP trunk lines help businesses lower communication costs by removing hardware expenses and offering pay-as-you-go channels. They also deliver clearer HD voice, flexible call routing across devices or locations, and quick scalability without new wiring or equipment.
- Cost Saving: You can avoid expensive hardware, installation fees, and ongoing maintenance. You only pay for the channels you use, which helps you reduce your overall communication cost.
- Higher Call Quality: VoIP-based trunking supports HD voice and improves clarity during calls. Since calls travel through the internet, you experience fewer interruptions and better audio quality.
- Better Call Routing: SIP trunks give you more control over how your calls move through your system. You can route calls to different devices, teams, or locations with simple settings instead of complex hardware changes.
- Effortless Scalability: You can easily add or remove channels in minutes. There is no need for new wiring or equipment, which makes SIP trunking ideal for growing businesses and remote teams.
Sign up with Calilio and Move Your Business Communication to a Smart, Sip-Powered Cloud System
What are the Challenges of Using Trunk Lines?
Traditional trunk lines come with challenges like physical wiring, limited scalability, and high upgrade costs, which make them harder to maintain as call volume grows. Modern setups ease some issues, but even VoIP trunk lines depend on strong internet and proper security to avoid call quality problems and cyber risks.
- Physical Dependency for Traditional Trunks: Traditional trunk lines require physical wiring, hardware, and on-site installation, making them more complex and expensive to maintain.
- Scaling Difficulty: Analog trunk lines support a fixed number of call channels. When the limit is reached, calls cannot go through unless more lines or hardware are added.
- Higher Upgrade and Maintenance Costs: Expanding capacity often means buying new equipment, installing additional cables, or upgrading PBX systems, which increases expenses.
- Location-based Restrictions: Traditional trunks tie your phone system to a single place, making them less flexible for remote teams, multi-branch operations, or hybrid work setups.
- Bandwidth Sensitivity: While VoIP trunk lines solve many traditional issues, they depend on a stable internet. Low bandwidth or network congestion can affect call quality.
- Security Considerations: VoIP trunks are often prone to cyber threats, so they need proper security setups, like firewalls, encryption, and access control, to protect against misuse or unauthorized access.
Conclusion
A trunk line remains an integral part of business communication, whether used in traditional systems or modern VoIP platforms. It helps companies manage multiple calls through a single connection, reduce costs, and simplify call handling. With the right provider and the correct trunking method, your phone system stays dependable and ready for whatever your business needs.
Calilio Introduces Affiliate Program
Earn 30% lifetime commission on every paid referral.
Turn your audience, network, or customers into a recurring revenue stream.

30% recurring commission on every paid referral

Lifetime earnings for as long as the customer stays subscribed

Unique referral link with real-time tracking

Perfect for agencies, consultants, creators, and SaaS partners

Frequently Asked Questions
Are trunk lines still used today?
Yes, trunk lines are still used today, especially in businesses that rely on traditional PBX systems or need stable, high-capacity calling. However, many organizations now prefer SIP and VoIP trunk lines because they offer lower costs, easier scaling, and better support for remote teams.
What is the difference between a trunk line and a landline?
Are trunk calls more expensive?

Still have questions?
Can’t find the answer you’re looking for? Please chat with our friendly team.
Stay in the loop
Get the latest call insights, trends, and updates delivered straight to your inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive updates from Calilio.
You can unsubscribe anytime.