What is IVR? Benefits, Types, Applications & Use Cases Explained

Summarize this blog with:
A growing business means a growing number of phone calls. And as teams expand, directing those calls to the right person or department becomes challenging. Plus, without the right system, callers’ waiting time increases, customer satisfaction drops, and eventually reduces operational efficiency.
That’s where Interactive Voice Response (IVR) comes in. IVR technology helps businesses streamline call management, reduce hold times, and improve customer service by automatically directing calls to the right place. It might be hard to believe, but IVR has existed since the 1960s.
Now, let’s learn what IVR is and its types. We will also look at its benefits and the best practices for implementing one for greater business success.
Key Highlights:
IVR technology enables automated customer interactions. It allows tasks like checking balances or reaching the correct agent/department without human assistance.
IVR systems reduce wait times, lower operational costs, and enhance customer experience with 24/7 availability and quick, self-service options.
There are different types of IVR, such as self-service, AI-powered, multi-language, and speech-enabled, offering flexibility for various business needs.
To enhance customer service, implement IVR with natural voices, simple menu options, live agent access, and multiple languages.
What is an Interactive Voice Response (IVR)?
An IVR is an automated telephony system or a part of a business phone system that interacts with callers using voice prompts and keypad inputs. When someone contacts your business, the IVR greets them, provides menu options, and directs their call to the correct department or self-service action, without requiring an agent to step in immediately.
In simple terms, an IVR acts as a smart virtual receptionist for effective call handling. In particular, it can answer common questions, collect customer information, route calls intelligently, and even complete tasks such as checking account details or scheduling callbacks. By automating these initial steps, an IVR streamlines communication, reduces wait times, and ensures every caller is guided efficiently from the moment they dial in.
Key Components of an IVR System
The key components of an IVR system include core elements like its call-connection framework, speech recognition, automated voice output, and keypad signal detection. Likewise, the advanced components include database access, call-center integration, conversational interpretation, call distribution, and analytical monitoring.
1. Core Components
- Telephony Interface: Serves as the bridge between the IVR and the phone network, managing call setup, signaling, and the flow of audio during interactions.
- Application Server: Runs the IVR software, processes caller inputs, and executes the logic that determines menus, prompts, and call routing decisions.
- Voice Recognition: Enables callers to speak commands instead of using keypad inputs, improving accessibility and speeding up interactions.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): TTS converts text into spoken words, allowing the IVR system to communicate effectively with the caller.
- DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency): These are the tones produced when a user presses a key on their phone to select options in the IVR menu.
2. Advanced Components
- Database Integration: Connects the IVR to CRM or internal databases so it can retrieve account details, authenticate callers, or update customer records.
- Computer Telephony Integration (CTI): Links the IVR with call center platforms, ensuring agents receive caller context and reducing the need for customers to repeat information.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enhances voice recognition by interpreting natural, conversational speech, creating a smoother and more intuitive user experience.
- Call Routing and Queuing: Organizes callers based on priority, skills, or departments and places them in queues when agents are busy, ensuring efficient call distribution.
- Analytics and Reporting Tools: Helps you monitor metrics like call flow, drop-off points, and menu performance, enabling businesses to continuously optimize their IVR system.
How Does an IVR System Work?
An IVR system operates by playing automated prompts after answering incoming calls. Then, it collects the caller’s spoken or keypad input and interprets it to determine the next step. And based on the input, it provides information, performs self-service tasks, accesses customer data, or passes the caller to the appropriate agent.
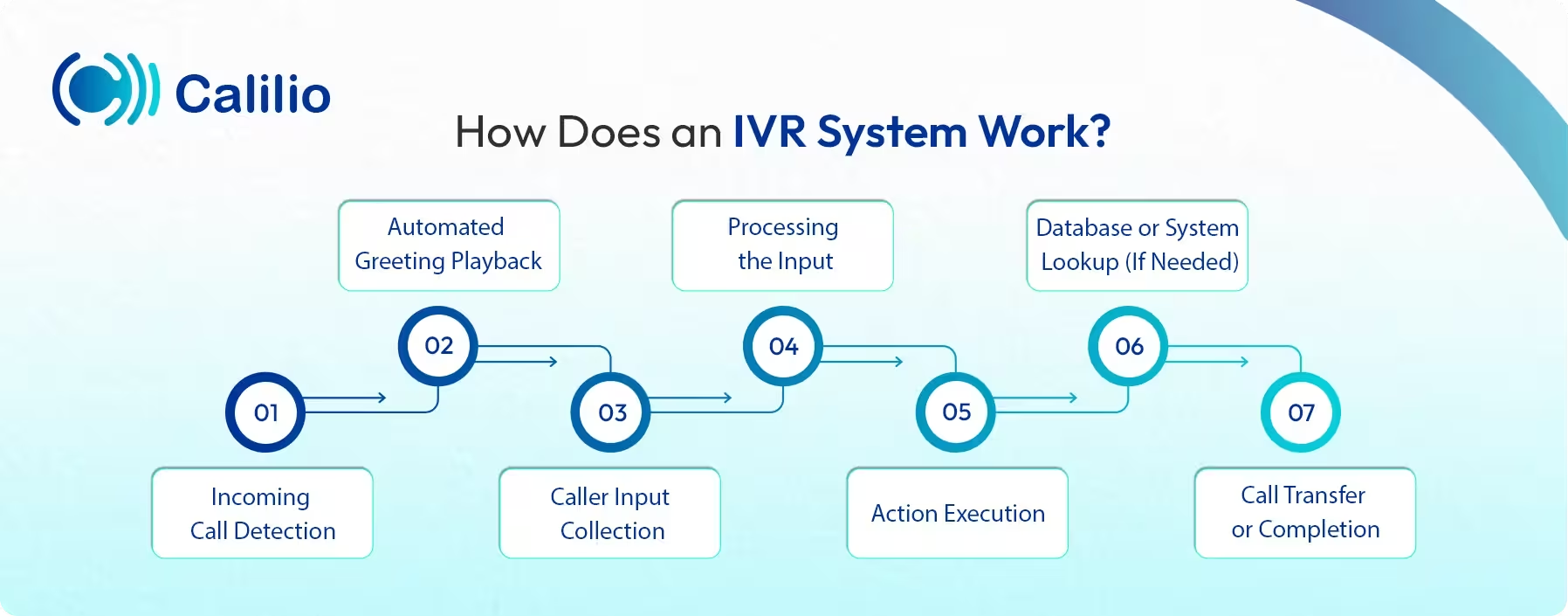
- Incoming Call Detection: When a caller dials your business number, the IVR connects through the telephony layer and immediately takes over the initial interaction.
- Automated Greeting Playback: The system plays a pre-recorded or TTS-generated welcome message that introduces menu options or instructions.
- Caller Input Collection: The caller responds using either voice commands or keypad selections, which the IVR interprets using speech recognition or DTMF detection.
- Processing the Input: The application server then evaluates the caller’s choice and decides the next step. For instance, call routing, providing information, or triggering another menu.
- Action Execution: Based on the input, the system may give an automated answer, perform a self-service task, or transfer the caller to the right agent or department.
- Database or System Lookup (If Needed): For tasks like checking account status or retrieving personal details, the IVR pulls relevant data from integrated databases or CRMs.
- Call Transfer or Completion: If the caller needs human support, the IVR hands off the call, often with CTI providing context to the agent. Otherwise, the IVR ends the interaction after delivering the requested information.
What are the Types of IVR Systems?
IVR systems can be categorized by how calls are handled, how callers interact with the system, and on the basis of automation features.
1. Based on Call Direction
- Inbound IVR: Manages incoming calls by greeting callers, presenting menu options, and directing them to the appropriate information or support team based on their selections.
- Outbound IVR: Automatically places calls to customers for reminders, alerts, surveys, appointment confirmations, or promotional campaigns, often without requiring agent involvement.
2. Based on the Interaction Method
- Basic/Touch-Tone IVR: Relies on keypad inputs where callers press specific numbers to navigate menus, making it simple, reliable, and widely supported across all phone types.
- Speech-enabled IVR: Allows callers to speak their choices rather than pressing buttons, using voice recognition technology to interpret commands and streamline the interaction.
- Visual IVR: Displays IVR menus on a smartphone or web interface. This means visual IVR enables users to tap through options quickly and avoid listening to lengthy or complex audio prompts
3. Based on Functionality and Complexity
- Multi-level IVR: Provides multiple layers of menus, guiding callers step-by-step through detailed options. So, multi-level IVR helps to reach the most relevant service or department.
- Self-service IVR: Offers automated solutions for everyday tasks like checking order status, verifying account details, or making payments, reducing the need for human assistance.
- Dynamic IVR: Adapts menu options and responses based on caller history, preferences, or context. As a result, dynamic IVR creates a more personalized and efficient experience.
- Location-based IVR: Routes calls or presents information based on the caller’s region or area code, helping businesses support multiple locations or languages.
- Time-based IVR: Adjusts its menus and routing rules according to business hours or time-sensitive conditions, ensuring callers always receive appropriate guidance.
- Hosted/Cloud-based IVR: Operates over the internet, reducing the need for on-premises hardware.
- Conversational IVR: Utilizes artificial intelligence to engage customers in natural dialogue, enhancing user experience.
Benefits of Implementing Interactive Voice Response
An IVR system improves customer service by offering quick, self-service options that reduce wait times. It also cuts operational costs by automating routine tasks and streamlining call routing. This allows agents to focus on complex issues.

1. Improved Customer Experience
An Interactive Voice Response system enhances customer experience by offering clear, easy-to-follow options. Customers can resolve simple issues independently and do not have to wait on the phone lines for live agents. If the options don’t address their problem, they can always speak with a representative for further assistance.
2. Cost Saving
IVR software helps lower operational costs by automating common tasks and reducing the need for live agents. Handling a call through an agent is more expensive, so businesses can save money by having the IVR telephone system manage simple queries. This frees up human resources for more complex customer concerns.
3. Faster Issue Resolution
Many businesses implement IVR to resolve issues that do not require agent support. With Interactive Voice Response technology, tasks like booking appointments or checking service status can be completed easily. Thus, your agents focus on more challenging issues, leading to faster resolution.
Connect Customers to the Right Experts with Calilio’s IVR System!
4. Anytime Availability
An Interactive Voice Response system operates 24/7, allowing consumers to access services anytime. Whether during business hours or after, the system ensures that customers can always interact with the firm. Clients can either retrieve information or leave messages, as needed. This level of availability helps businesses support customers across different time zones.
5. Streamlined Call Routing
An IVR system simplifies call management by directing customers to the correct department or service. In traditional phone systems, calls can be misdirected. However, Interactive Voice Response software ensures that callers are guided to the right options. This avoids frustration and makes the call-routing process more efficient.
Use Cases & Applications of the IVR System
Banking, healthcare, e-commerce, and more sectors use IVR to automate customer interactions and improve service efficiency. From handling routine inquiries to routing calls, IVR plays a key role in streamlining communication in any industry.
Banking & Finance
In the banking and finance sector, IVR, also known as phone tree systems, allows customers to check balances, make payments, or report lost cards. The IVR system can perform the mentioned tasks without waiting for a human representative. Likewise, banks also usually authenticate customers by asking for their card or account number through IVR to ensure security.
Call Center
IVR in call centers provides several advantages. They automate data collection during customer interactions, ensuring accuracy and consistency. IVR systems also efficiently route calls to the correct department. This cuts down on hold times and speeds up service. Additionally, IVR operates 24/7 and provides customer service anytime, even outside business hours.
Medical, Healthcare & Pharmacy
IVR in healthcare helps streamline patient services. For instance, patients can easily schedule, confirm, or cancel appointments with just a few button presses. They can also get basic health information without speaking to anyone.
Ecommerce
In e-commerce, IVR systems help customers track orders and get real-time updates. They automatically confirm orders and provide estimated delivery times. Customers can also get status updates on shipments and change their orders, all through simple voice commands or keypad inputs.
Travel & Hospitality
IVR systems effectively allow people to check details on room availability, booking options, and check-in/check-out times. Airlines use IVR for flight status updates and booking modifications, while hotels rely on it for reservations and information.
Conclusion
IVR systems evolved from being simple call routers to powerful tools for enhancing customer service. When implemented with thoughtful design and best practices, they reduce wait times, cut costs, and improve caller satisfaction. Regardless of the industry, a well-optimized IVR ensures that customers are heard, valued, and supported.
However, setting up and managing a standalone IVR system can be challenging. Businesses often deal with complex configurations, maintenance issues, hardware costs, and limited scalability. Because of this, many are shifting to cloud telephony platforms with built-in IVR features, which offer a more straightforward setup, remote management, automatic updates, and greater flexibility.
Calilio Introduces Affiliate Program
Earn 30% lifetime commission on every paid referral.
Turn your audience, network, or customers into a recurring revenue stream.

30% recurring commission on every paid referral

Lifetime earnings for as long as the customer stays subscribed

Unique referral link with real-time tracking

Perfect for agencies, consultants, creators, and SaaS partners

Frequently Asked Questions
Is IVR easy to set up and use?
Yes, especially with cloud-based systems. Modern IVR platforms offer drag-and-drop builders and preconfigured templates, making setup quick and user-friendly.
How much does an Interactive Voice Response system cost?
Are IVR calls recorded?
Is IVR still relevant today?
What is the difference between VoIP and IVR?

Still have questions?
Can’t find the answer you’re looking for? Please chat with our friendly team.
Stay in the loop
Get the latest call insights, trends, and updates delivered straight to your inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive updates from Calilio.
You can unsubscribe anytime.